

The resulting environment provides multiple paths for storage traffic to flow from an ESXi host to the storage array to a LUN. Virtual machine files are stored in VMFS. LUNs are owned by one or both storage controllers depending on your array architecture. These ports are cabled to the Ethernet switches in a highly available manner. Each storage controller has two or more front-end ports for host connectivity. These switches should be capable of handling the expected amount of traffic necessary for the I/O activity of all the virtual machines' storage traffic.īusiness-class storage arrays typically contain two or more storage controllers (A and B sides) for high availability. These NICs are connected to a pair of Ethernet switches. For iSCSI, this means that two or more 1GbE or 10GbE NICs should be available in each physical ESXi host. The physical servers should have two or more storage adapters. Those hosts access the same shared storage datastores. In a typical vSphere environment, we combine two or more servers that have VMware ESXi installed into a cluster. As such, iSCSI should be connected in a highly available manner. Note: Redundancy is important to a reliable VMware vSphere environment. Virtual Machines are stored in the VMFS datastore. ESXi formats the LUN with the VMware File System (VMFS). We’ll focus on iSCSI for the remainder of this walkthrough.ĮSXi hosts connect to iSCSI SANs using either 1Gb or 10Gb Ethernet connections. ESXi supports Fiber Channel (FC), Fiber Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) or iSCSI SANs.
#VMWARE VSPHERE 6.5 INTRODUCTION PLUS#
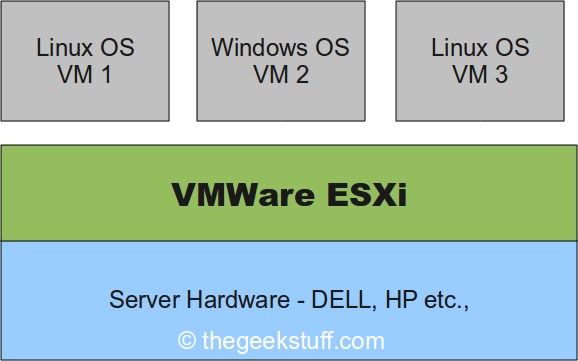
Block-based storage, plus the storage adapters (HBA) and storage fabric (switches and cabling) are known as a Storage Area Network, or SAN. The hosts are responsible for formatting and creating a file system on that space. In block storage, the storage array presents a raw set of hard drive blocks called a Logical Unit (LUN) to the connected hosts. VMware ESXi can mount file-based storage using the NFS protocol. In file storage, the storage array (sometimes called a filer) creates and owns a file system, presenting the file system to a host to use. This storage can be presented to ESXi hosts using either file or block-based storage protocols. VMware vSAN aggregates a mix of solid state and magnetic internal hard drives of multiple physical servers into a logical, highly available, high performance datastore.Īn external storage array is another option for providing shared storage to multiple ESXi hosts. Shared storage can be provided in several different ways. Shared storage provides a common pool of storage for clustered hosts to access, enabling advanced vSphere features. When multiple ESXi servers are clustered together, we can take advantage of VMware vMotion, High Availability (HA) and Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS) to provide enhanced functionality, availability and manageability. While this is acceptable for a single-server environment, a single server’s internal disks do not provide highly available storage, nor does this solution scale well. Internal hard-drives in a stand-alone ESXi host can be used to host VMware Virtual Machine files including configuration files and virtual hard drives. Use the arrow keys to navigate through the screens.īefore we walkthrough the configuration of iSCSI, let’s review some storage basics. This walkthrough demonstrates the concept of shared storage in a vSphere with Operations Management environment.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
